Usignal¶
-
class
pylayers.signal.bsignal.Usignal(x=array([], dtype=float64), y=array([], dtype=float64), label=[])[source]¶ Bases:
pylayers.signal.bsignal.BsignalSignal with an embedded uniform Base
This class inheritate from Bsignal. The only difference is that the x base is supposed to be uniform
Methods Summary
abs()return the absolute value of an Usignal
alignc(u2)align 2 Usignal
dx()get the time step of Usignal.x
energy([axis])calculate the energy of an Usignal
eprfl([axis])Energy profile
expand(a)expand the time support by a scale factor a
fftshift()max()maximum of Usignal
min()minimum of Usignal
resample(x_new[, kind])resample the Usignal with a new x base
setx(start, stop, dx)set the x array of the Usignal (y=0)
truncate(imin, imax[, axis])truncate USignal in range [posmin, posmax]
width()get the extension support of the Usignal
window([win])windowing Usignal Parameters ———-
zleft(xmin)add zeros on the left until xmin
zlr(xmin, xmax)add zeros to the left and to the right
zright(xmax)add zeros on the right until xmax
Methods Documentation
-
alignc(u2)[source]¶ align 2 Usignal
alignc <=> intersection alignc : align two Usignal on a same base
return a list which contains the two aligned signals
- LUsignal
concatenated signal L1.y and L2.y
-
dx()[source]¶ get the time step of Usignal.x
>>> from pylayers.signal.bsignal import * >>> u = Usignal() >>> u.setx(0,10,0.1) >>> assert(u.dx()==0.1)
-
eprfl(axis=-1)[source]¶ Energy profile
axis : int
if axis==0
$$delta_x sum_l |y(l,k)|^2$$
if axis==1
$$delta_x sum_k |y(l,k)|^2$$
cut
-
expand(a)[source]¶ expand the time support by a scale factor a
- afloat
expansion factor
Usignal : support extended signal
return a new Usignal with expanded factor a
-
resample(x_new, kind='linear')[source]¶ resample the Usignal with a new x base
x_new needs to be strictly included in the original x base of the Usignal.
x is a 1D array y is a 2D array
if y is complex the interpolation is done on module and unwrapped phase separately
x_new : ndarray kind : string
‘linear’ |’spline’
-
setx(start, stop, dx)[source]¶ set the x array of the Usignal (y=0)
start : float stop : float dx : float
>>> u = Usignal() >>> u.setx(0,10,0.1)
-
truncate(imin, imax, axis=-1)[source]¶ truncate USignal in range [posmin, posmax]
imin : int imax : int axis : axis to truncate (default -1)
Usignal
-
width()[source]¶ get the extension support of the Usignal
width is conventionnaly equal to the difference between extremities + dx
w : float
-
window(win='hamming')[source]¶ windowing Usignal Parameters ———-
- winstring
window type (‘hamming’,’blackman’,’hanning’)
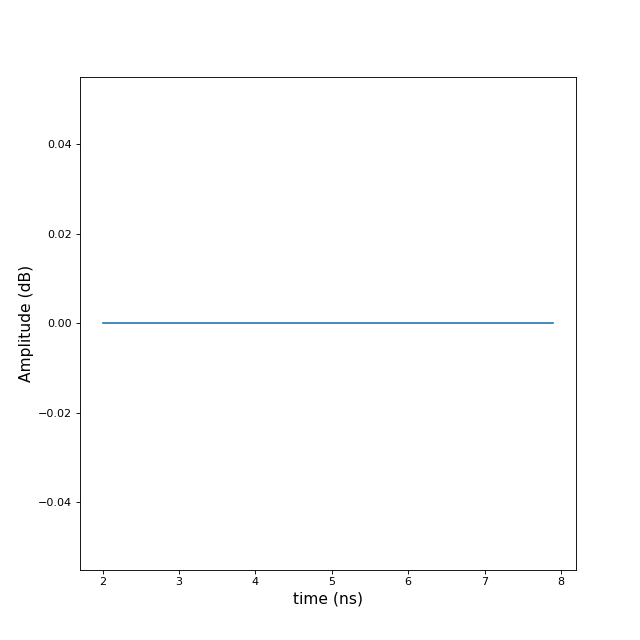
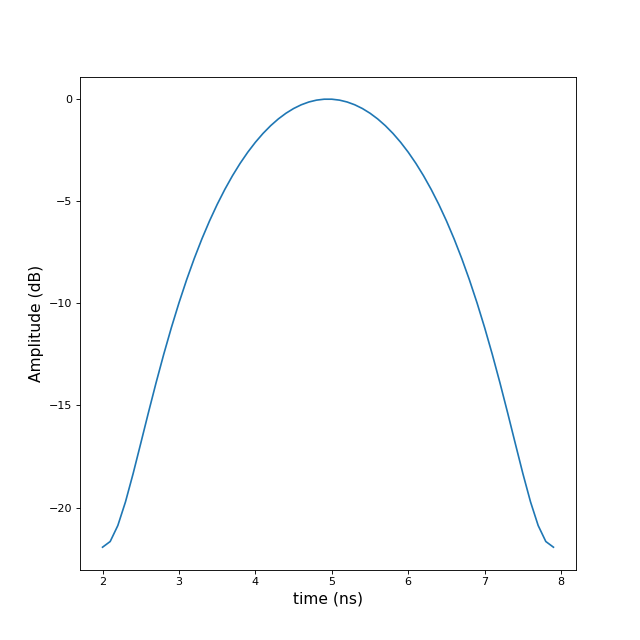
>>> import numpy as np >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> from pylayers.signal.bsignal import * >>> x = np.arange(2,8,0.1) >>> y = np.ones(len(x)) >>> U = Usignal(x,y) >>> fig,ax = U.plot() >>> U.window('hamming') >>> fig,ax = U.plot()
-
zlr(xmin, xmax)[source]¶ add zeros to the left and to the right
- xminfloat
add zeros before xmin
- xmaxfloat
add zeros after xmax
This corresponds to a gating between xmin and xmax
>>> from pylayers.signal.bsignal import * >>> from matplotlib.pylab import * >>> ip = TUsignal() >>> ip.EnImpulse() >>> f,a = ip.plot(typ=['v']) >>> ip.zlr(-10,10) >>> f,a = ip.plot(typ=['v'])
-