SlabDB¶
-
class
pylayers.antprop.slab.SlabDB(fileslab='', filemat='', ds={}, dm={'AIR': {'epr': (1+0j), 'mur': (1+0j), 'roughness': 0.0, 'sigma': 0.0}, 'METAL': {'epr': (1+0j), 'mur': (1+0j), 'roughness': 0.0, 'sigma': 10000000}, '_AIR': {'epr': (1+0j), 'mur': (1+0j), 'roughness': 0.0, 'sigma': 0.0}})[source]¶ Bases:
dictSlab data base
DB : slab dictionnary
Methods Summary
add(name, lmatname, lthick[, color])add a slab from its properties
addgui(name)add a slab in the DB
delete(name)delete an element from the database
edit(name)edit a Slab in the DB
load([_fileini])Load a Material from a .ini file
save([_fileini])save SlabDB in a .ini file
show([name, fGHz])evaluate and show a given slab
showall()show all slabs
Methods Documentation
-
add(name, lmatname, lthick, color='black')[source]¶ add a slab from its properties
name : string lmatname : list of mat name lthick : list ot float
list of layer thickness in meters
Examples from the paper:
“Reflection and Transmission Properties of Building Materials in D-Band for Modeling Future mm-Wave Communication Systems ” Martin Jacob and Thomas Kurner and Robert Geise and Radoslaw Piesiewicz EUCAP 2010
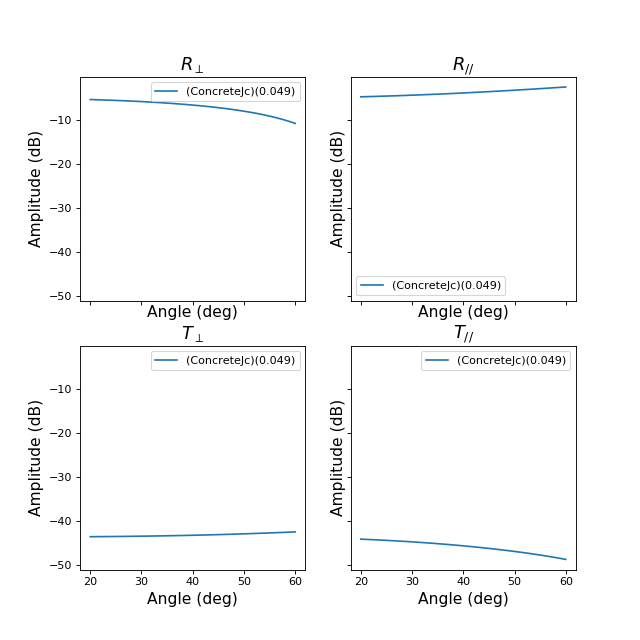
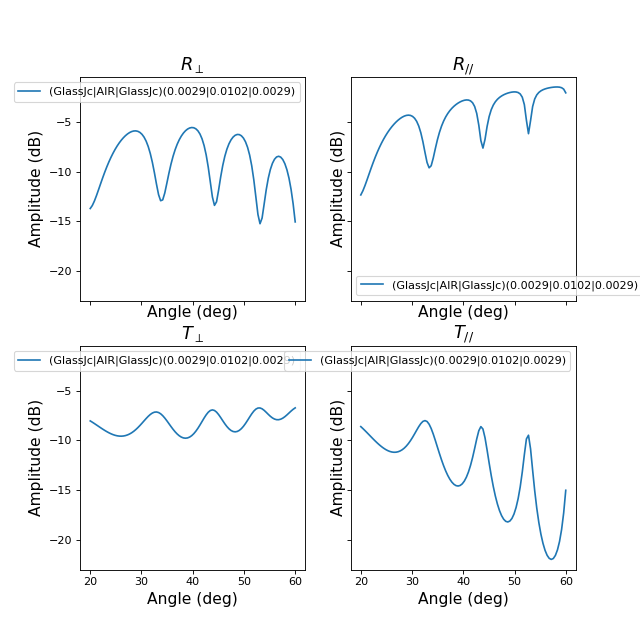
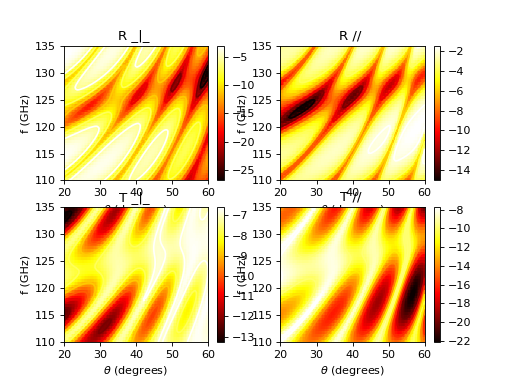
>>> from pylayers.antprop.slab import * >>> import numpy as np >>> import matplotlib.pylab as plt >>> sl = SlabDB(filemat='matDB.ini',fileslab='slabDB.ini') >>> sl.mat.add(name='ConcreteJc',cval=3.5,alpha_cmm1=1.9,fGHz=120,typ='THz') >>> sl.mat.add(name='GlassJc',cval=2.55,alpha_cmm1=2.4,fGHz=120,typ='THz') >>> sl.add('ConcreteJc',['ConcreteJc'],[0.049]) >>> sl.add('DoubleGlass',['GlassJc','AIR','GlassJc'],[0.0029,0.0102,0.0029]) >>> theta = np.linspace(20,60,100)*np.pi/180 >>> sl['ConcreteJc'].eval(120,theta) >>> f,a=sl['ConcreteJc'].plotwrt(var='a',typ=['l20']) >>> fig = plt.figure() >>> sl['DoubleGlass'].eval(120,theta) >>> f,a = sl['DoubleGlass'].plotwrt(var='a',typ=['l20']) >>> freq = np.linspace(110,135,50) >>> fig = plt.figure() >>> sl['DoubleGlass'].eval(freq,theta) >>> sl['DoubleGlass'].pcolor(dB=True)
Exemple from paper “[Kiani2007] Glass Characterization for Designing Frequency Selective Surfaces to Improve Transmission through Energy saving glass windows Kiani 2007” The surface impedance is \(R = 4 \Omega\), the thicknesss is \(d = 100 nm\)
Pilkington Spectrum OnLine applet
Design of Energy Saving Windows with high Transmission at 900MHz and 1800 MHz
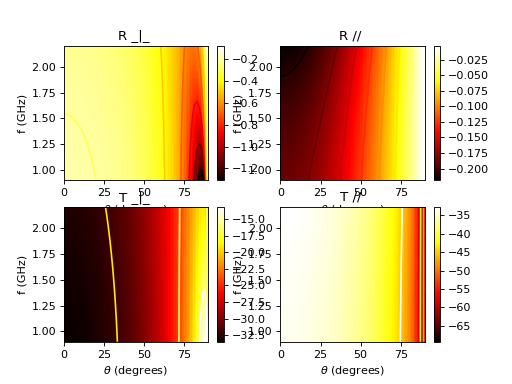
\[\sigma = \frac{1}{Rd} = 2.5 10^{6} S/m\]>>> from pylayers.antprop.slab import * >>> import numpy as np >>> import matplotlib.pylab as plt >>> sl = SlabDB(filemat='matDB.ini',fileslab='slabDB.ini') >>> sl.mat.add(name='CoatingPilkington',cval=1,sigma=2.5e6,typ='epsr') >>> sl.mat.add(name='GlassPilkington',cval = 6.9,sigma = 5e-4,typ='epsr') >>> sl.add('Optitherm382',['CoatingPilkington','GlassPilkington'],[100e-9,0.00382]) >>> fGHz = np.linspace(0.9,2.2,50) >>> theta = np.linspace(0,np.pi/2,100) >>> sl['Optitherm382'].eval(fGHz,theta) >>> sl['Optitherm382'].pcolor(dB=True)
-